VAI TRÒ CỦA CỘNG HƯỞNG TỪ ĐÀN HỒI 3 TESLA TRONG ĐÁNH GIÁ ĐỘ XƠ HÓA GAN
12/10/2023 10:53:06 | 0 binh luận
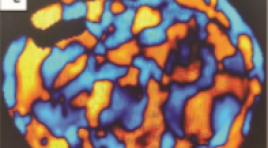
SUMMARY Objectives: To investigate liver fibrosis using magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) and the relationship between MRE and histopathology in the assessment of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic viral hepatitis. Methods: Retrospective study, description, investigation of the liver by MRE before biopsy in 20 patients with chronic viral hepatitis in Cho Ray Hospital from 11/2019 to 05/2021. Results: The mean age is 51.4 years and 100% of patients are female. The mean liver stiffness (kilopascal = kPa) is 3.1 ± 0.2 (F1, n = 8), 3.6 ± 0.1 (F2, n = 11), 5.3 (F3, n = 1) respectively. The Spearman correlation coefficient is 0.63 (p=0.003), which shows a strong correlation between the liver stiffness measured with MRE and the fibrosis on the liver biopsy sample evaluated by the Metavir scoring system. Based on the ROC curve and the cut-off value of 3.7 kPa, it can be predicted that there is a presence of significant fibrosis (≥ F2), a sensitivity of 58%, and a specificity of 100%. Conclusions: MRE is a safe and non-invasive technique that can replace biopsy in the assessment of the liver fibrosis stage. Keywords: Magnetic resonance elastography, stiffness, liver fibrosis, chronic viral hepatitis, histopathology.
ĐẶC ĐIỂM HÌNH ẢNH SIÊU ÂM VÀ CẮT LỚP VI TÍNH TRONG CHẨN ĐOÁN VIÊM TÚI THỪA MANH TRÀNG
11/10/2023 14:31:15 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objectives: Describe the characteristics of ultrasound images and computed tomography in the diagnosis of cecal diverticulitis. Subjects and methods : A cross-sectional study on 49 patients who underwent ultrasound and computed tomography at the Center of Radiology in Bach Mai Hospital, diagnosed with cecal diverticulitis on CT, was treated at Bach Mai Hospital from June 2020 to June 2021. Results: ultrasound showed diverticulum 63.3%, inside diverticulum there was fecal stone 18.3%, gas or fecal content 18.3%, fluid 26.5%, diverticulum wall thickness (>2mm) 28.6%, cecal wall thickness 95.9%, fat infiltration around the diverticulum or caecum 81.6%. 47/49 patients had thickened cecal wall, 89.8% thickened around the circumference. CT scan, 71.4% had 1 diverticulum, 20.4% had multiple diverticula, 10.2% had gas in the diverticulum, 55.1% had fecal stones, 26.5% had fluid in the diverticulum, thickened diverticulum (>2mm) 71.4%, 95.9% thickening of the cecum wall. Conclusions : Ultrasonography and CT imaging are very valuable imaging tools for determining the diagnosis, extent of lesions and complications of cecal diverticulitis, and are meaningful in clinical practice for choosing treatment methods. Keywords: cecal diverticulitis, ultrasound, computed tomography

Cộng hưởng từ đàn hồi gan: Nguyên lý, kỹ thuật, và ứng dụng lâm sàng
25/08/2021 12:33:44 | 0 binh luận

Vai trò của chụp cắt lớp vi tnh trong đánh giá mạch máu thận của người cho thận sống trước phẫu thuật ghép thận
25/08/2021 12:47:45 | 0 binh luận
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"