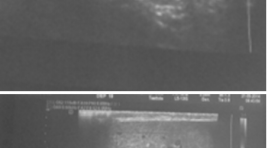
Đặc điểm hình ảnh siêu âm Triplex trong chẩn đoán xoắn tinh hoàn tại bệnh viện Việt Đức
01/04/2020 13:52:07 | 0 binh luận
Describe the characteristics of the Triplex ultrasound images of testicular torsion at Viet Duc hospital SUMMARY Purpsose: Describe the Triplex ultrasound imaging characteristics of testicular torsion Object and methods: Patients who have acute scrotum going to Viet Duc Hospital Emergency Sonography Department between March 2014 and September 2005, were diagnosed testicular torsion and operated. Results : 32 cases were diagnosed as testicular torsion, diagnosis after surgery is correct 100% of the cases. The mean age 19,2 ± 5,1. Sign “whirlpool” is found in 75% of cases, the common position is above the testicles 91.7%. Sign of losing the pulse signal at testicular torsion 31/32 (96.9%). Increased testicular size 27/32 (84.4%). 28/32 heterogeneous parenchyma, normal 3/32, 1/32 hypoechoic. Epididymis morphology change 25/32 cases (78.1%), of which the most common are sphere 76%. Conclusions: Triplex Ultrasonography has value in the different diagnosis of testicular torsion with other diseases causing scrotal pain. Keywords : Triplex sonography, testicular torsion.
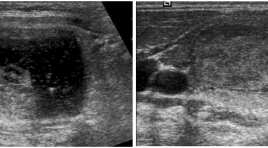
Nghiên cứu ứng dụng phân loại TIRADS trong chẩn đoán tổn thương dạng nốt tuyến giáp trên siêu âm
01/04/2020 11:48:16 | 0 binh luận
Application of thyroid imaging reporting and data system (TIRADS) in evaluation of thyroid nodules on ultrasound imaging SUMMARY Objectives : To describe sonographic findings of thyroid focal lesions and to evaluate the role of Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TIRADS) in predicting the malignancy of thyroid focal lesions. Material and methods: Prospective study on 180 patients. Thyroid focal lesions were scored by using TIRADS. The sonographic findings were compared with pathological results. Results: Solid was the most sensitive sonographic indicator of malignancy (93.8%), while the most specific indicator was the taller-than-wide sign (98.2%). The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and accuracy of TIRADS in predicting the malignancy of thyroid focal lesions were 87.5%, 92.1%, 51.9%, 98.7% and 91.7%, respectively. Conclusion: TIRADS is a simple score which is easy to apply in clinical practice with high diagnostic accuracy. Keywords: Thyroid nodules, ultrasound
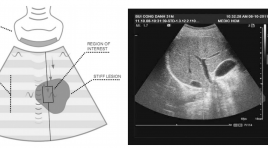
Tổng quan công nghệ và ưu thế vượt trội của kỉ thuật siêu âm đàn hồi ARFI
01/04/2020 10:09:04 | 0 binh luận
Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging

Ứng dụng siêu âm trong chẩn đoán, theo dõi tiến triển và đánh giá kết quả điều trị tinh hoàn không xuống bìu ở trẻ dưới 2 tuổi
01/04/2020 08:46:03 | 0 binh luận
Application of ultrasound in diagnosis, monitoring progess and evaluating treatment outcomes cryptochidism in children under 2 years of age SUMMARY Cryptorchidism is the most common urological genital malformation in children.Ultrasound is a good radiology method for diagnosis and treatment evaluation. We have performed a research with name “Application of ultrasound in diagnosis, monitoring progess and evaluating treatment outcomes cryptochidism in children under 2 years of age”. The study included 69 patients, was carried out from October 2012 to August 2013 . The sensitivity ultrasound in diagnosis is between 60- 100% denpending on each position. Ultrasound diagnoses testicle dimension properly in comparison with surgery. Success rate after surgery, three months of endocrinology treatment, six months of endocrinology treatment are 94.6%, 25% and 40% respectively. Key words: cryptochidism, ultrasound.
Đánh giá tình trạng co mạch não ở bệnh nhân xuất huyết dưới nhện bằng siêu âm doppler xuyên sọ
31/03/2020 15:36:51 | 0 binh luận
summary Subarachnoid hemorrage (SAH) is common emergency in patients who got the congenital or acquaired cranio-vascular diseases. This results from some reasons such as: aneurysm ruption, AVM or trauma. Vasospasm increases disability and mortality in patients who have SAH. Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound (TCD) is the good method to diagnose early this stage with many advantages as non-invasive, cheaply, the sensitivity and specification is rather high. Purpose : 1. Evaluating the vasospasm after SAH by TCD; 2. Researching the correlation between the level SAH as well as the clinical state of patients and the velocity blood flow of the middle cerebral artery recorded by TCD. Subjects and methods : We have prospected 20 patients who were diagnosed SAH on Computed tomography. TCD was performed 2 times: the 3rd – 4th day and the 8th – 9th day after getting SAH. Those whose peak systolic velocity in middle cerebral artery was ≥ 120cm/s considered vasospasm. Their clinical states were also recorded at the same times. Results : 2 patients (10%) got vasospasm of MCA at the 8th – 9th day after SAH. The correlation between the level SAH as well as the clinical state of patients and the velocity blood flow of MCA is unclosed. Conclusion : TCD can detect early the vasospasm but the accuracy of this method is higher in the patients whose SAH is primary and non - operated.
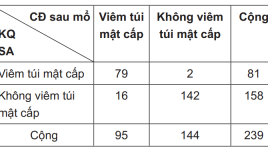
Vai trò siêu âm trong chẩn đoán sỏi túi mật, viêm túi mật cấp có đối chiếu kết quả PT và mô bệnh học
03/04/2020 12:49:49 | 0 binh luận
Ultrasonic role in diagnosis gallstones and acute cholecystitis summa ry Objectives: Assess the role of ultrasound through the determination of the sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive and negative predictive value in the diagnosis of gallstones, acute cholecystitis (compared with the results of the surgery and the pathology). Methods: Retrospective, cross-sectional description. Results : From January to June 2012, 239 patients were included in the study. Ultrasound diagnosis of 184 patients with gallbladder stone, 81 acute cholecystitis. Postoperative diagnosis 192 patients with gallbladder stones, acute cholecystitis 95 patients. Anatopathologic result get 39 acute cholecystitis. Conclusions: Ultrasound diagnosis of gallbladder stone had a Sn of 95.31%, Sp 98.87%, Acc 95.81%, PPV of 99.46% (in comparison with surgery).Ultrasound diagnosis of acute cholecystitis had a Sn of 87.18% , Sp of 76.50%, Acc 78.24%, PPV of 41.98% (in comparison with anato- pathology). Key words : Ultrasound, gallstones, cholecystitis.
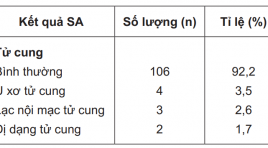
Nghiên cứu giá trị của siêu âm bơm dịch trong chẩn đoán bất thường tử cung - vòi tử cung ở các trường hợp vô sinh
03/04/2020 12:41:58 | 0 binh luận
Assessment of uterine cavity and Fallopian tube patency by sonohystero graphy with saline solution summa ry Introduction : Fallopian tube damage is a common cause, accounting for 30 - 40% of infertile women. Assessment of uterine cavity and Fallopian tube patency is a routine indication with hystero-salpingo graphy (HSG). This technique potentially has risk of allergy, X-ray exposure and specificity is not optimal. This research aims to evaluate the application of vaginal ultrasound combined pumping saline solution into the uterus to examine Study design: cross-sectional descriptive study in 115 cases with infertility examined at Hue University Hospital through clinical examination, gynecological transvaginal ultrasound, pumping normal saline into the uterus and then did HSG at the same period. Results : The abnormalities detected in 30.4% (35/115) cases of infertility. In 11 cases have abnormal uterine cavity diagnosed by ultrasound, HSG detected only 5 cases. The rate of abnormal sonohysterography results are quite good compared to HSG (19.1% vs 17.4%). However, ultrasound can not determine the position occlusion of tube. A number of factors such as age over 35 (p = 0.02; OR = 2.87; CI95%: 1.11 to 7.48), urban residents (p = 0.01), secondary infertility (p = 0.001; OR = 4.21; CI95%: 1.82 to 9.76), chlamydia infection (p = 0.01, OR = 13.17; CI95%:) and high pressure pumping (p = 0.00; OR=17.11) increased the rate of abnormal sonohysterography scan. The rate of complications caused by ultrasound is lower than by HSG. Disadvantages of sonohysterography with saline is impossible to identify the position of tubal occlusion if it does not pass through the end of tube. Conclusion : HSG with saline is a simple method, inexpensivepensive and very effective to assess the uterine cavity and tubal patency in cases with infertility, with similar results compare to HSG and even offer further detection of genital abnormalities which are missed by HSG.
Đánh giá kết quả siêu âm doppler xuyên sọ trong chẩn đoán chết não tại bệnh viện Trung Ương Huế
23/05/2020 11:07:39 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Background : Although the clinical examination has the most important role and documentation of the clinical signs of brain death are very uniform, it is necessary to use technical confirmatory tests to corroborate the clinical signs such as Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography (TCD) and Electroencephalography (EEG). The current study examined (1) Hemodynamic of cerebral arteries in 16 death brain cases (2) the role of TCD in confirmation of brain death. Subjects and methods :16 patients clinical brain deathwere included in the study. The following TCD findings were accepted as confirmatory of brain death when they were found at least one of two within the same examination: (1) brief systolic forward flow or systolic spikes and diastolic reverse flow or no diastolic flow, (2) Vmax <10cm/s or no demonstrable flow in a patient in whom flow had been clearly documented in a previous TCD examination. Results : All of cases were confirmed as brain death on TCD. 14/16 patients (87.5%) performed the waveform abnormality, the rest was found decreasing velocity or missing the blood flow on TCD. Conclusion: The sensitivity of TCD is increased with repeat examinations and should be repeated in cases in which systolodiastolic forward flow is demonstrated after the first TCD. TCD may prolong or shorten the time to declaration of brain death. The necessity of demonstrating cerebral circulatory arrest in patients with clinical brain death is debatable. Key words: brain death, doppler ultrasonography.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"