NGHIÊN CỨU GIÁ TRỊ CỦA CHUỖI XUNG TƯỚI MÁU VÀ CHUỖI XUNG PHỔ TRÊN CỘNG HƯỞNG TỪ 3 TESLA CHẨN ĐOÁN PHÂN BẬC U THẦN KINH ĐỆM
18/10/2023 10:03:50 | 0 binh luận
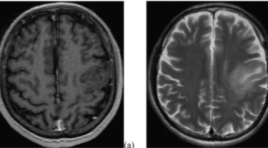
SUMMARY Purpose: To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance spectroscopy and dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) magnetic resonance perfusion for glioma grading. Materials and Methods: Fifteen patient confirmed pathological glioma who underwent MR spectroscopy and DCE in 3 Tesla MRI machine. The following parameters were used: Ktrans, Ve, Cho/NAA, Cho/Cre. The diagnostic accuracy for glioma grading was determined by ROC analysis. Results: There were 10 patients in the high-grade group and 5 patients in the low-grade group. Ktrans, Ve, Cho/NAA and Cho/Cre measures differed significantly between high and low-grade tumor. The AUC was 0.956 for Ktrans. Conclusion: Ktrans, Ve Cho/NAA and Cho/Cre parameters demonstrated to be useful for glioma grading. Keywords: Spectroscopy, DCE-MRI, glioma grading
KINH NGHIỆM BƯỚC ĐẦU TRONG ĐIỀU TRỊ ĐỘT QUỴ THIẾU MÁU NÃO CẤP DO TẮC ĐỘNG MẠCH NÃO LỚN BẰNG KỸ THUẬT SOLUMBRA TẠI BỆNH VIỆN CHỢ RẪY
12/10/2023 15:35:10 | 0 binh luận
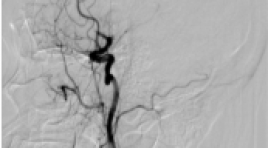
SUMMARY Background: Mechanical thrombectomy is considered the firstline treatment method for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) due to large vessel occlusion (LVO). Two current main techniques include stent retriever and direct aspiration. Recently, endovascular treatment for AIS has reached a great progression, in which the Solumbra technique, a combination of stent retriever and direct aspiration techniques, has been introduced to achieve high rate of recanalization, to minimize the occurrence of distal embolization and to improve clinical outcomes. We reported initial experience utilizing Solumbra technique at Cho Ray Hospital. Materials and Methods: Case series report of patients with acute ischemic stroke treated by Solumbra technique at Choray Hospital, from 01/2019 to 01/2021. Clinical, angiographic and outcome features were collected and evaluated. Results: There were 23 cases treated by Solumbra technique: the mean age was 72 years old, mean NIHSS at admission was 19, good recanalization rate of TICI 2b-3 was achieved in 18/23 (78.3%), functional independence outcomes (90-day mRS 0-2) was 10/23 (43.5%) patients. The embolization to new territories (ENT) was 2/23 (8.7%), the rate of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH) was 4/23 (17.4%) and mortality rate was 3/23 (13%) patients during follow-up. The average time from arterial puncture to recanalization was 37.3 minutes. Conclusion: Mechanical thrombectomy using Solumbra technique appeared to be a fast, safe and effective method with high recanalization rate and good clinical outcomes. Solumbra would be a promising technique to reduce thrombus fragmentation and distal embolization. Key words: Acute ischemic stroke, large vessel occlusion, endovascular treatment, Solumbra technique.
NGHIÊN CỨU MỐI LIÊN QUAN GIỮA SUY GIẢM NHẬN THỨC VÀ SA SÚT TRÍ TUỆ VỚI TỔN THƯƠNG NÃO TRÊN CỘNG HƯỞNG TỪ
12/10/2023 13:01:23 | 0 binh luận
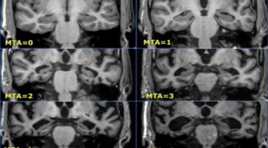
SUMMARY Purpose: To study the association between cognitive impairment, dementia, and brain features on magnetic resonance imaging. Retrospective and Prospective study: A cross-sectional descriptive study with 100 patients above 60 years, made MMSE and tested a brain MRI at Quang Tri Provincial General Hospital from 1/2021 to 10/2021. Results: In 100 studied patients, tested by MMSE, 38% had normal cognitive status, 51% had mild cognitive impairment, and 11% had dementia. Cognitive decline is associated with age but not sex. Cognitive impairment and dementia are associated with global brain atrophy, medial temporal cephalic atrophy, frontal lobe atrophy, parietal lobe atrophy, and occipital lobe atrophy but not white matter hyperintensities (small vessel disease) and lacunar infarction. The higher the GCA (global cortical atrophy scale), the higher the MTA (mesial temporal atrophy scale), and the more severe the cognitive impairment. Conclusion: Magnetic resonance imaging is a strongly important role in the diagnosis of cognitive decline and dementia, with features such as total cerebral atrophy, medial temporal brain atrophy, parietal lobe atrophy, frontal lobe atrophy, and occipital lobes atrophy are all involved in the patient's cognitive status, and the assessment of these features on magnetic resonance imaging help to the early diagnosis and prediction of future dementia. Keyword: Dementia, mild cognitive impairment, magnetic resonance imaging
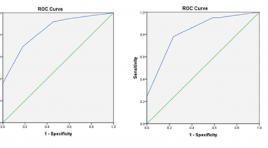
ÁP DỤNG BẢNG PHÂN LOẠI CAD-RADS TRONG ĐÁNH GIÁ BỆNH ĐỘNG MẠCH VÀNH MẠN TÍNH TRÊN CẮT LỚP VI TÍNH ĐA DÃY
16/11/2021 11:19:01 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Purpose: To apply the CAD-RADS classification in the assessment of chronic coronary artery disease on multislice computed tomography. Material and methods: Cross-sectional description of 179 patients undergoing coronary computed tomography angiography, diagnosed according to CAD-RADS classification by two physicians independently, the intra-class correlation was used to test the inter-reviewer agreement (IRA), and comparing with results invasive coronary angiography. Results: There was an excellent IRA between the two for CADRADS (κ=0.904), by each CAD-RADS classification (κ=0.827-1.00), by coronary artery stenosis (κ=0.878-0.931). There is an excellent IRA for modifiers G (κ=1), and S (κ=1), moderate IRA for V (κ=0.574). The best cutoff value for predicting significant CAD was ≥ CAD-RADS 3. The diagnostic value of CAD-RADS classification according to the common segment: sensitivity 77.54%, specificity 87.23%, positive predictive value 89.92%, negative predictive value 72.56%. Conclusion: There is an excellent inter-reviewer agreement when applying the CAD-RADS classification to clinical practice, with high sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy when compared with invasive coronary angiography. Keywords: coronary artery, CAD-RADS, CT angiography, graft, stent
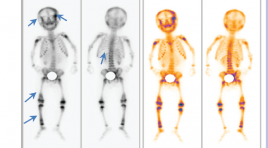
NGHIÊN CỨU ĐẶC ĐIỂM XẠ HÌNH XƯƠNG VỚI 99mTc-MDP TRONG BỆNH U NGUYÊN BÀO THẦN KINH TẠI BỆNH VIỆN NHI TRUNG ƯƠNG TỪ THÁNG 1/2018 - 03/2020
15/11/2021 17:13:57 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective: To determine the proportion of bone metastasis and whole-body scintigraphy with 99mTc-MDP in neuroblastoma (NB) in children. Subjects and Methods: A retrospective descriptive combined prospective study was conducted on 86 patients under 15 years old, diagnosed with NB according to the standards of Pediatric Oncologists Conference in 1988 and had whole-body scintigraphy with 99mTc-MDP at Vietnam National Children's Hospitalfrom January 2018 to March 2020. Results: The proportion of detection metastasis was 33.7%. There are 55.2% patients with bone metastases without clinical manifestations (without bone pain). 100% cases of bone metastases on whole-body scintigraphy have images of increased radioactivity. Most of the patients were about 2 - 4 years old 58.6%, lower limb position 62.1%, multifocal lesions 72.4%, of which 58.6% patients had over 5 lesions. Conclusions: Whole-body scintigraphy with 99mTc-MDP is a valuable technique for detecting bone metastases on NB in the early stage when absence of clinical manifestations of bone metastases. Keywords: Neuroblastoma, whole-body scintigraphy, 99mTc-MDP.
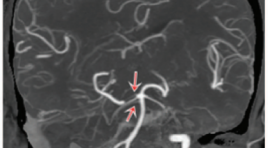
Mô tả bất thường giải phẫu nửa sau vòng động mạch não trên chụp cắt lớp vi tính
06/05/2021 16:04:23 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Objective: To describe the anatomical variations in posterior half of the circle of Willis and to determine the rate of the anatomical variability of these arteries. Materials and Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study in 480 people who were performed CT angiography of the cerebral arteries at the University Medical Center Hospital between January 2019 and December 2020. The blood vessels to be investigated included: posterior communicating arteries, posterior cerebral arteries, basal artery, anterior inferior cerebellar arteries, posterior inferior cerebellar arteries, and the superior cerebellar artery. A radiologist who had more than 5 years of experience of CT brain evaluates these anatomical variations: hypoplasia, aplasia, fetal type, fenestration, duplication, triplication and double origin. Results: The study was composed of 480 people (259 males, 221 females). The mean age of people was 55.7 ± 16.7 years (range, 2 - 102 years). 50 - 69 age group accounts for the majority with 237 people (49.4%). The anatomical variations of posterior communicating artery: unilateral hypoplasia 38.5%, bilateral hypoplasia 19.4%, unilateral aplasia 22.9%, bilateral aplasia 4.0%, fenestration 0.4%. The anatomical variations of posterior cerebral artery: unilateral hypoplasia 10.2%, bilateral hypoplasia 3.5%, unilateral aplasia 8.8%, bilateral aplasia 1.3%, unilateral fetal 17.9%, bilateral fetal 5%. The anatomical variations of basal artery: hypoplasia 5.6%, aplasia 0%, fenestration 0.6%. The anatomical variations of anterior inferior cerebellar artery: unilateral aplasia 30%, bilateral aplasia 10.4%, unilateral duplication 1.3%, bilateral duplication 5.8%, triplication 0.2%. The anatomical variations of posterior inferior cerebellar artery: unilateral aplasia 29%, bilateral aplasia 5.8%, unilateral duplication 0.4%, bilateral duplication 0%, fenestration 0.2%, double origin 0.2%. The anatomical variations of the superior cerebellar artery: aplasia 0%, unilateral duplication 11.3%, bilateral duplication 2.9%, triplication 1.7%, double origin 0.4%. Conclusion : The anatomical variations in posterior half of the circle of Willis are common. The most common abnormalities are the fetal type of posterior cerebral artery, hypoplasia or aplasia of the posterior communicating artery, hypoplasia or aplasia anterior and posterior inferior cerebellar artery, and the duplication of the superior cerebellar artery. Keywords: posterior circulatory system, computed tomography, anatomical variations.
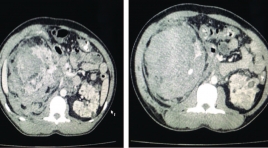
U thận trong bệnh cảnh phakomatosis, những điều cần lưu ý: nhân hai trường hợp lâm sàng
05/12/2019 10:06:36 | 0 binh luận
Renal tumors in the Phakomatosis disease, what to note: two case report SUMMARY Phakomatosis are a group of neurocutaneous disorders characterised by involvement of structures that arise from the embryonic ectoderm , consist of central nervous system, skin ,eyes and others: kidney, heart, lung… In this article we focus on the incidence of renal tumors in Tuberous sclerosis, one of the common diseases in Phakomatosis. Tuberous sclerosis is a rare neurocutaneous disorder (phakomatosis) characterized by the development of multiple benign tumours in various organs, including the kidneys. Tuberous sclerosis complex has several renal manifestations including angiomyolipomas (AML) and renal epithelial neoplasms. Angiomyolipomas is found in 40% of patients with tuberous sclerosis, and its most common complication is ruptures due to aneurysms. We present two cases was diagnosed with bilateral angiomyolipomas in tuberculosis and emphasizes the importance of the diagnosis and choice of appropriate treatment for each patient. Key words : Phakomatosis, renal tumor
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
- Ca lâm sàng: điều trị ung thư tuyến giáp bằng I-131
- Những tiến bộ trong chẩn đoán hình ảnh bệnh tim – mạch
- Ứng dụng CNTT trong chẩn đoán hình ảnh giúp tăng chất lượng y tế
- CA LÂM SÀNG: UNG THƯ BIỂU MÔ NỘI ỐNG TUYẾN VÚ
- KẾT QUẢ ỨNG DỤNG XẠ HÌNH THẬN ĐỘNG TẠI BỆNH VIỆN NHI ĐỒNG THÀNH PHỐ
- NGHIÊN CỨU BƯỚC ĐẦU ĐÁNH GIÁ VAI TRÒ CỦA TRÍ TUỆ NHÂN TẠO TRONG PHÂN TÍCH KẾT QUẢ X QUANG NGỰC THẲNG TẠI BỆNH VIỆN CHỢ RẪY
- NGHIÊN CỨU ĐẶC ĐIỂM HÌNH ẢNH VÀ VAI TRÒ CỦA SIÊU ÂM TRONG CHẨN ĐOÁN U TUYẾN CẬN GIÁP
- ĐÁNH GIÁ KẾT QUẢ BƯỚC ĐẦU ĐIỀU TRỊ TĂNG SẢN LÀNH TÍNH TUYẾN TIỀN LIỆT CÓ BÍ TIỂU CẤP BẰNG PHƯƠNG PHÁP CAN THIỆP NÚT ĐỘNG MẠCH TUYẾN TIỀN LIỆT
- VỠ TÚI GIẢ PHÌNH KHỔNG LỒ TÂM THẤT TRÁI: BÁO CÁO 1 TRƯỜNG HỢP HIẾM GẶP TẠI BỆNH VIỆN BẠCH MAI
- VAI TRÒ CỦA SINH THIẾT BẰNG KIM LÕI DƯỚI HƯỚNG DẪN SIÊU ÂM TRONG ĐÁNH GIÁ HẠCH CỔ BẤT THƯỜNG
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"