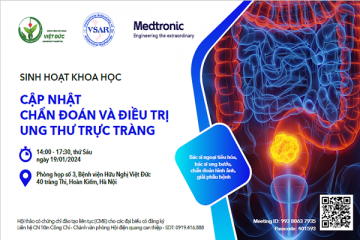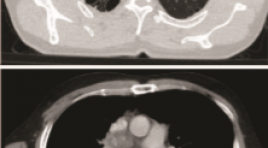
BÁO CÁO CA BỆNH: SINH THIẾT U PHỔI DƯỚI HƯỚNG DẪN SIÊU ÂM
17/10/2023 16:42:23 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY The ultrasound-guided transthoracic biopsies are indicated for pulmonary masses or mediastinal masses located in the periphery adjacent to the pleural-thoracic surface and pleural lesions. We present a case where the lung tumor was anterior to the scapula with emphysema. Keywords: Transthoracic biopsy, Ultrasound-guided transthoracic biopsies, lung tumor
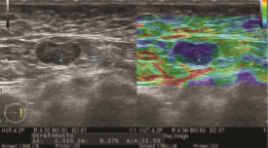
NGHIÊN CỨU GIÁ TRỊ CỦA SIÊU ÂM ĐÀN HỒI MÔ NÉN TRONG CHẨN ĐOÁN HẠCH NÁCH ÁC TÍNH
13/10/2023 12:33:32 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Purpose: To evaluate the accuracy of strain elastography in the diagnosis of malignant axillary lymph nodes. Methods: B-mode and strain elastography US were scanned by experienced radiologists on patients with clinical symptoms or suspicion of breast cancer to look for masses or abnormal lymph node. Lymph nodes are evaluated on B-mode ultrasound based on 4 factors: short and long axis diameter, hilum, and cortical thickening. The strain elastography was based on a color scale of 1 to 5 points based on percentage of nodal region on the color chart, and a semi-quantitative B/A index of node stiffness correlation with adipose tissue of the same depth. Results: a total of 41 lympho nodes (benign, n=13, malignant, n=28) from 39 patients were analyzed. B-mode ultrasonography in the evaluation of malignancy had a sensitivity and specificity of 67.9% and 69.2%. Strain elastography for assessment of axillary lymph node involvement had a sensitivity and specificity of 85.7% and 69.2%. The semi-quantitative index B/A had statistically significant difference between the group of benign and malignant lymph nodes (p<0.05) with the cut of is 23.5. Conclusion: Strain elastography is a non-invasive and helpful method, together with B-mode ultrasound, in the evaluation of malignant axillary lymph node involvement. K ey words: axillary lymph node, strain elastography
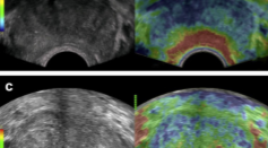
CẬP NHẬN VAI TRÒ CỦA SIÊU ÂM ĐÀN HỒI TRONG CHẨN ĐOÁN UNG THƯ TUYẾN TIỀN LIỆT
12/10/2023 15:57:29 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Prostate cancer (PC) is an emerging male health problem in recent years due to new development in diagnostic and treatment modalities that help improve disease prognostic, especially in Eastern countries where PC incidence is high. According to GLOBOCAN 2020, number of new cases of PC reached 1,414,259 while number of deaths was 375,304 cases. In terms of deaths due to cancer in male population, prostate cancer ranks two just after lung cancer. Together with the traditional trio of rectal exam, Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) and transrectal ultrasound, emerging imaging modalities such as elastography ultrasound, multimodality magnetic resonance imaging not only helped physicians better detecting malignant lesions at supra early stage but also guided biopsy for pathological assessment. These new innovations led to preference of target-biopsy with lower rate of re-biopsy and complications comparing to systemic biopsy technique
Nghiên cứu đặc điểm hình ảnh và giá trị siêu âm trong chẩn đoán hạch cổ ác tính
06/05/2021 14:14:26 | 0 binh luận
SUMMARY Background : The purpose of the study was to evaluate the characters and efficacy of B Mode and color Doppler ultrasound (CDUS) in diagnosis malignant cervical lymph nodes. Materials and Methods: In this cross-sectional prospective study, during a period of 12 months, performed on 85 patients including two groups: group I includes 63 patients with cervical lymphadenopathy with suspected lymph nodes on US and group II includes 22 patients with clinically suspected lymph nodes (not have any suspicious characteristics in US) were prospectively evaluated with B-mode and CDUS. Statistical analysis was carried out with histopathological or cytological diagnosis as gold standard. Results: We conducted ultrasound in 85 patients,. To compare with the pathology results of the disease, there are 56 metastatic lymph nodes, 04 lymphoma nodes, 01 plasmocyoma lymph node, 18 nonspecific inflammatory lymph nodes, 01 purulent lymph node and 05 granulomatous lymph nodes due to tuberculosis. The sensitivity, specificity, the accuracy of 2D ultrasound method combined with Dopper ultrasound are 95.08%, 79,2 %, 92%, 86% và 90,6%. Conclusions : Within the limitations of this study, B-mode and CDUS evaluations were found to be highly significant with a high sensitivity and specificity. B-mode and CDUS examinations provide a prospect to reduce the need for biopsy/fine needle aspiration cytology in reactive nodes. Keywords: B-mode ultrasound, Doppler color ultrasonography, histopathology, lymph node.
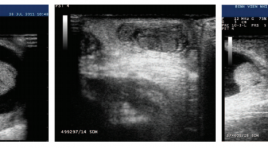
Đặc điểm lâm sàng và siêu âm xoắn tinh hoàn chu sinh báo cáo loạt ca và hồi cứu y văn
02/06/2020 09:46:31 | 0 binh luận
Perinatal testicular torsion clinical and sonographics findings SUMMARY Objective: Perinatal testicular torsion either occurring prenatally in utero or postnatally in the first month of life, is surgical emergency with hope salvaging of testis. A challenge to clinicians and radiologist. With sonographics findings as small size of testis, heterogenous echostructure, thickened tunica albuginea with rim hyperechoic (calcification), to suggest testicular torsion. Methods: Cases report Results : From January 2015 to May 2019, we had 11 patients with perinatal testicular torsion introduced into the study batch. The average age is 8.2 days. One song twists on two sides, on the left 7 shifts. The time of detection after birth, an average of 1.5 days, no cases of prenatal ultrasound were detected. The average time of hospital admission is 17 days. 100% normal birth, full month.Ultrasound signs: testicular big size 7/12 (58.3%), heterogeneous parenchyma structure 11/12 (91.7%), calcareous membrane calcification 2/12 (16.6%), hydrocephalus, heterogeneous fluid, 7/12 fibrin (58.3%), enlarged stalks, edema 3/12 (25%). Mark Whirpool positive 8/12 (67%), central blood loss 11/12 (91.7%). The rate of testicular removal is 10/12 (83.3%). Conclusions: Twisted perinatal testicular, rare surgical emergency, causes purple swelling of the scrotum and requires early diagnosis and surgical intervention. High-value color doppler ultrasound determines testicular twisting and eliminates the causes of swelling and pain in the scrotum. Keywords: testicular torsion, neonate, ultrasound.
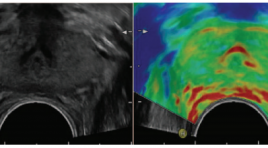
Siêu âm đàn hồi trong chẩn đoán ung thư tuyến tiền liệt: đánh giá bước đầu qua 101 trường hợp
02/06/2020 09:42:08 | 0 binh luận
Transrectal sonoelastography in detection of prostatecancer: initial assessment of 101 cases SUMMARY Purpose Evaluate the efficiency of transrectal strain elastography (SE) and transrectal B-mode ultrasonography (TRUS) in determining prostate cancer. Material & Methods From 20/6/2015 to 10/9/2015, There are 101 patients with PSA level of higher 4ng/ml have been selected. Abnormal echo regions in prostate were found via conventional TRUS in those patients, then Abnormal echo regions would be evaluated by real-time strain ultrasound elastography. Patients have undergone six core biopsies by transperineal approach. Experimental studies Results Comparising between 3 methods: B-mode TRUS, strain elastography and DRE about sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV). (table) Table.Comparising between 3 methods: B-mode TRUS, strain elastography and DRE. Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) PPV (%) NPV (%) B-mode 88.5 55.1 67.6 81.8 Strain-elasto 94.2 65.3 74.2 91.4 DRE 69.2 98 98 75 Conclusions: Sonoelastographyprovidesmore information to detect prostate cancer and biopsy guidance. SE reached a higher sensitivity and specificity than B-mode US in the detection prostate cancer.Strain ultrasound elastography can be used as routine as colour Doppler. Key words: sonelastography, strain ultrasound elastography, prostate cancer, ultrasound.
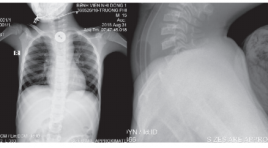
Đặc điểm siêu âm dị vật tiêu hóa trên ở trẻ em được can thiệp lấy dị vật tại Bệnh viện Nhi Đồng 1 báo cáo loạt ca
02/06/2020 09:16:09 | 0 binh luận
Ultrasound of foreign bodies in gastrointestinal tract removed at Children’s Hospital 1 case report SUMMARY Objectives : We reviewed ultrasound features of all cases of foreign bodies in the upper gastrointestinal tract that underwent endoscopic or surgical removal at Children’s Hospital N1 from 1/2018 to 4/2019. Method : retrospective case. Results : From 1/2018 to 4/2019, 7 cases were included. Mean age was 7,9 years old. Boy to girl ratio was 5/2. 5/7 cases were radiolucent foreign bodies, toothpick mostly. The positions were one oesophageal, 2 gastric và 4 duodenal. All cases were diagnosed correctly by ultrasound before intervention. 4/7 cases underwent surgical removal, 3 cases underwent endoscopic removal. The signs of right-side retroperitoneal oedema and fluid collection surrounding right kidney on ultrasound were highly suspected of posterior D3 duodenal wall perforation due to foreign bodies. Conclusion: Foreign bodies in the upper gastrointestinal tract can cause dangerous complications in case of late diagnosis. Ultrasound can help find radiolucent as well as radiopaque objects. We should know typical ultrasound features of some foreign bodies and common sites of complication in order to predict the object and the location exactly to give proper management. Key words : foreign bodies, ultrasound, children.
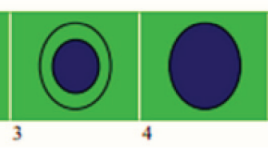
Nghiên cứu so sánh siêu âm đàn hồi strain elastography (se) so với shearwave elastography (swe) trong bệnh lý u vú nữ tại Medic TPHCM 2019
01/06/2020 17:32:09 | 0 binh luận
A comparative study of strain elastography (se) and shear wave elastography (swe) in female breast tumor disease at medic medical center in HCMC in 2019 SUMMARY Objective: Combining B-mode US, BI-RADS classification and applying 2 types of elastography: Strain Elastography (SE) and Shear Wave Elastography (SWE) on RS85 ultrasound scanner (Samsung) in diagnosis of benign/ malignant breast tumors. Detecting diagnostic value for each method and when combining them. Materials and methods: Selecting female breast tumors that classified Birads 3,4,5 by B-mode US, examining elastography at the same time by 2 methods: SE and SWE using L2-9MHz probe on RS85 ultrasound scanner (Samsung) from August to October, 2019 at Medic Medical Center in HCMC. Collecting data of 2 types of Elastography: SE: collecting 3 values: (1) color mapped elastogram according to Tsukuba elasticity score, (2) E/B ratio (the largest transversal diameter that hardest color - coded on the color map / the largest transversal diameter of tumor on B-mode US) (<1 or >1), (3) ratio B/A (A= tumor lesion, B= normal fat tissue above the lesion). SWE: measuring the tissue stiffness (kPa) and shear wave velocity (m/s) (according to color-coded tumor stiffness map, selecting the hardest point that satisfied RMI (reability measurment index) ≥ 0.4. Measuring each method 3 times on the same tumor. Bi-rads 3-4-5 lesions undergone biopsy (FNAC and/ or core biopsy) to have determined diagnosis. Then calculating the diagnostic value of each method and when combining the 2 methods. Using the SPSS 20 software for statistics and analyzing. Results: The study has 84 breast tumors (51 benign and 33 malignant) that have determined diagnosis by cytology and histology. Strain Elastography value: 1.1. Choosing color map according to Tsukuba elasticity score from 1→5 in diagnosis has sensitivity (90%), specificity (88.2%), positive predictive value (83%), negative predictive value (93.8%), accuracy (8.3%)1.2. Choosing the E/B ratio (the largest transversal diameter that hardest color - coded on the color map / the largest transversal diameter of tumor on B-mode US) value (that <1 suspected benign tumor and ≥ 1 suspected malignancy) has sensitivity (87%), specificity (90.2%), positive predictive value (85.3%), negative predictive value (92%), accuracy (89.3%) 1.3. The ratio of mean strain elastography value of malignant and benignbreast tumor / fat tissue are (8.1+/- 3.7) and (2.4+/-1.3) (p<0,001).The ratio at cut-off value (3.2) has the highest sensitivity (97%) and specificity (84.3%) in diagnosing malignant breast tumors. Area under the ROC curve calculated (0.969). Positive predictive value (80%). Accuracy (89.3%). 2. Shear wave elastography (SWE) value: 2.1. Shear wave mean velocity of benign and malignant tumor groups are (3.9 ± 1.1) and (5.9 ± 1.3) (m/s) (p<0,001). Mean ratio at the cut-off value (4.2m/s) has the highest sensitivity (90.9%) and specificity (66.7%) in diagnosing malignant breast tumors. Area under the ROC curve calculated (0.873).Positive predictive value (63.8%). Negative predictive value (91.8%). Accuracy (76.2%). 2.2. Mean stiffness value of benign and malignant breast tumor groups are (49.7 ± 28.2) and (108±4.5) (kPa) (p<0,001). Mean ratio at the cut-off value (50.3 kPa) has sensitivity (90.9%), specificity (66.7%). Area under the ROC curve calculated (0.864), positive predictive value (61.2%), negative predictive value (91.4%), accuracy (73.8%) 3. Combination of SE and SWE value Combining the 2 types of elastography SE and SWE in diagnosing breast tumor by evaluating E/B of SE and shear wave velocity (m/s) of SWE increases the strongly sensitivity (100%), specificity (52,9%) and positive predictive value (57,9%), negative predictive value (100%), accuracy (71,4%), helps to reduce unnecessary biopsied cases. Conclusions: SE and SWE are useful in diagnosing breast tumor. Combining the 2 types of elastography SE and SWE have strongly sensitivity, helps to reduce unnecessary biopsied cases.
Bạn Đọc Quan tâm
- Ca lâm sàng: điều trị ung thư tuyến giáp bằng I-131
- Những tiến bộ trong chẩn đoán hình ảnh bệnh tim – mạch
- Ứng dụng CNTT trong chẩn đoán hình ảnh giúp tăng chất lượng y tế
- CA LÂM SÀNG: UNG THƯ BIỂU MÔ NỘI ỐNG TUYẾN VÚ
- KẾT QUẢ ỨNG DỤNG XẠ HÌNH THẬN ĐỘNG TẠI BỆNH VIỆN NHI ĐỒNG THÀNH PHỐ
- NGHIÊN CỨU BƯỚC ĐẦU ĐÁNH GIÁ VAI TRÒ CỦA TRÍ TUỆ NHÂN TẠO TRONG PHÂN TÍCH KẾT QUẢ X QUANG NGỰC THẲNG TẠI BỆNH VIỆN CHỢ RẪY
- NGHIÊN CỨU ĐẶC ĐIỂM HÌNH ẢNH VÀ VAI TRÒ CỦA SIÊU ÂM TRONG CHẨN ĐOÁN U TUYẾN CẬN GIÁP
- ĐÁNH GIÁ KẾT QUẢ BƯỚC ĐẦU ĐIỀU TRỊ TĂNG SẢN LÀNH TÍNH TUYẾN TIỀN LIỆT CÓ BÍ TIỂU CẤP BẰNG PHƯƠNG PHÁP CAN THIỆP NÚT ĐỘNG MẠCH TUYẾN TIỀN LIỆT
- VỠ TÚI GIẢ PHÌNH KHỔNG LỒ TÂM THẤT TRÁI: BÁO CÁO 1 TRƯỜNG HỢP HIẾM GẶP TẠI BỆNH VIỆN BẠCH MAI
- VAI TRÒ CỦA SINH THIẾT BẰNG KIM LÕI DƯỚI HƯỚNG DẪN SIÊU ÂM TRONG ĐÁNH GIÁ HẠCH CỔ BẤT THƯỜNG
Sự kiện sắp diễn ra
Thông tin đào tạo
- Những cạm bẫy trong CĐHA vú và vai trò của trí tuệ nhân tạo
- Hội thảo trực tuyến "Cắt lớp vi tính đếm Photon: từ lý thuyết tới thực tiễn lâm sàng”
- CHƯƠNG TRÌNH ĐÀO TẠO LIÊN TỤC VỀ HÌNH ẢNH HỌC THẦN KINH: BÀI 3: U não trong trục
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Cập nhật RSNA 2021: Công nghệ mới trong Kỷ nguyên mới"
- Danh sách học viên đạt chứng chỉ CME khóa học "Đánh giá chức năng thất phải trên siêu âm đánh dấu mô cơ tim"